Want to clone a GitHub repository on Windows? Learn the easy step-by-step process for 2026 using Git Bash, Command Line, and GitHub Desktop.
If you want to work on a project locally, learn from open-source code, or contribute to a team project, you must know how to clone a repository from GitHub on Windows.
We guarantee you this process is simpler than it sounds—even if you’re a complete beginner. In fact, cloning is often the very first step developers take after discovering a useful GitHub project.
When you clone a GitHub repository, you create a full local copy of the project on your Windows PC. As a result, you can explore files, run the project, make changes safely, pull updates, and collaborate without affecting the original repository.

This workflow mirrors how real-world development teams operate across companies, startups, and open-source communities.
This guide walks you through every step, using the command line, GitHub Desktop, and Visual Studio Code, so you can choose the method that works best for you. Whether you prefer Git Bash, PowerShell, or a GUI-based approach, you’ll end this guide with a working local repository.
What is a GitHub Repository and What Does “Git Clone” Actually Do?
A GitHub repository is an online storage space where developers keep all the files, code, documentation, and configuration related to a project. More importantly, it tracks changes over time using Git’s version control system. This allows teams to collaborate, review history, and revert mistakes when needed.
For example, popular services and frameworks such as Visual Studio Code, Docker documentation, and many WordPress plugins all rely on GitHub repositories. When you access these repositories, you are viewing the central project source.
When you clone a repository, you copy the entire project from GitHub to your local Windows computer. This includes:
- All files and folders
- Every branch (main/master and feature branches)
- Complete commit history
- The hidden .git folder used for version control
That .git folder plays a crucial role because it stores metadata, commit history, remote URLs, and branch information. Thanks to this folder, Git knows how to pull, fetch, push, checkout branches, and authenticate with GitHub.
Unlike downloading a ZIP file, cloning keeps the repository linked to GitHub. Because of that connection, you can update your project with git pull, contribute changes, and sync your work with others. In professional environments, developers almost always clone repositories instead of downloading ZIP files.
Why You Should Clone a GitHub Repository Instead of Downloading
You should clone a GitHub repository if you want to:
- Work locally using tools like Visual Studio Code or IntelliJ IDEA
- Learn and experiment with real-world production code
- Contribute to open-source projects using pull requests
- Collaborate with a team while keeping changes isolated
- Maintain backups with full version history
- Work offline and sync changes later
For instance, if you want to study how authentication works in a real application, cloning lets you explore folders, inspect commits, and test changes locally. Similarly, companies often share private GitHub repositories with new employees, and cloning becomes the fastest way to start working on assigned tasks.
Therefore, we recommend cloning instead of downloading whenever you plan to build, modify, or maintain a project.
Prerequisites: How to Install Git on Windows and Prepare Your Environment
Before you clone a repository from GitHub on Windows, you should prepare your environment properly. This preparation reduces errors such as authentication failures or command not found issues.
Step 1: Install Git on Windows (Git Bash & CMD)
Git is the core tool that enables cloning, branching, and version tracking. GitHub works with Git, not instead of it.
You can install Git in two ways:
- Download Git for Windows from the official website
- Or install it using Windows Package Manager:
winget install git
After installation, Git becomes available in Git Bash, PowerShell, and Command Prompt (CMD). Git Bash often feels more comfortable for beginners because it behaves like a Linux terminal, which many Git tutorials reference.
To confirm installation, run:
git --version
If Git returns a version number, your system is ready.
Step 2: Configure Git Identity (User Name & Email)
Before your first clone or commit, you must introduce yourself to Git. If you skip this, Git will repeatedly prompt you or fail when you try to save changes. Run these commands once in your terminal:
git config --global user.name "Your Name" git config --global user.email "your.email@example.com"
Ensure the email matches your GitHub account email to properly attribute your contributions.
Step 3: Choose Your Tool: Git Bash, PowerShell, or GitHub Desktop
On Windows, you can clone repositories using:
- Git Bash / PowerShell / Command Prompt (CLI approach)
- GitHub Desktop App (GUI approach)
- Visual Studio Code (Integrated Editor approach)
Both options use the same Git engine. However, developers often prefer CLI for speed and scripting, while beginners and designers often choose GitHub Desktop for its visual workflow.
Method 1: How to Clone a GitHub Repository Using Command Line (Git Bash, PowerShell, CMD)
This method works in Git Bash, PowerShell, or CMD and remains the most widely used approach in real-world development teams.
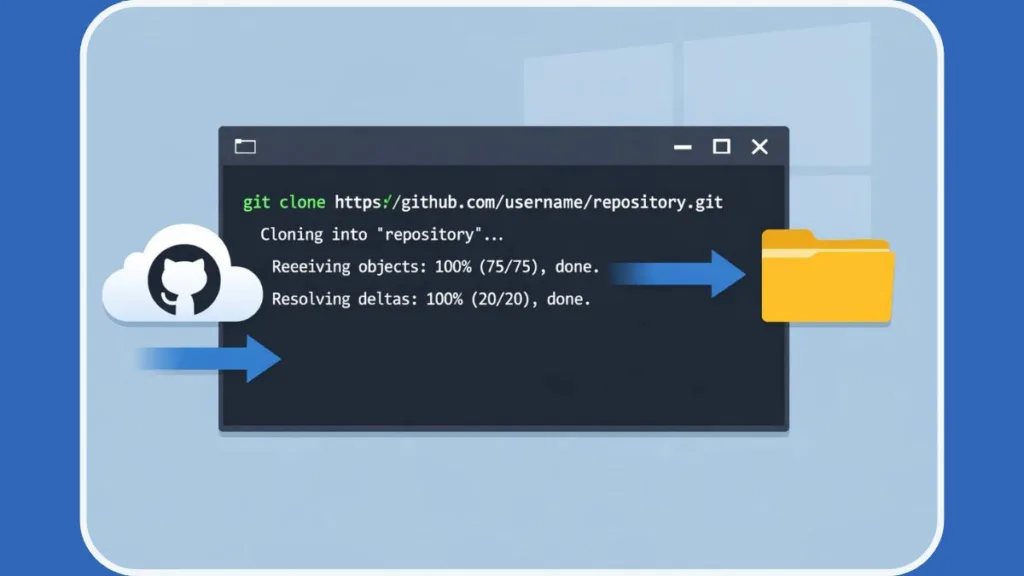
1. Open Git Bash, PowerShell, or Windows Terminal
Open Git Bash from the Start menu, or launch PowerShell or Windows Terminal. If you use Visual Studio Code, you can open its integrated terminal and run Git commands there as well.
2. Navigate to Your Desired Local Folder
Navigate to the folder where you want the project saved:
cd %USERPROFILE%\Desktop
Because Git clones into the current local directory, this step determines where your files appear. Many developers create folders like Projects or Work to keep repositories organized.
3. Locate the Target Repository on GitHub
Visit the repository’s main page on GitHub. This repository may be public, private, or forked from another project.
4. Copy the Repository URL (HTTPS vs. SSH)
Click the Code button and copy the URL:
- HTTPS for simplicity and compatibility (Recommended for beginners)
- SSH if you’ve configured SSH keys and 2FA
Note on Password Authentication: GitHub removed support for password authentication in 2021. If you use HTTPS, you may need to sign in via a browser prompt or use a Personal Access Token (PAT) instead of your password.
5. Run the Git Clone Command in Windows
git clone https://github.com/username/repository.git
6. Verify Your Local Repository Clone
Press Enter. Git downloads the full repository, initializes the .git folder, and creates a new directory.
To verify the files are actually there, you can run:
ls (in Git Bash) or dir (in Command Prompt)
You can now open the project in Visual Studio Code or any IDE and start working immediately.
How to Clone an Empty GitHub Repository on Windows
An empty repository contains no files or commits. Developers often create empty repositories when starting new projects.
- Open the repository on GitHub
- Under Quick setup, copy the HTTPS or SSH URL
- Run:
git clone https://github.com/username/repository.git
Git still initializes the repository locally. Afterward, you can add files, commit changes, and push them to GitHub.
Method 2: How to Clone a Repository Using GitHub Desktop (GUI Guide)
If you prefer a visual interface, GitHub Desktop offers a clean and beginner-friendly experience.
1. Launch GitHub Desktop and Sign In
Sign in using your GitHub account. Authentication happens automatically through the app, saving you from managing SSH keys manually.
2. Select “Clone Repository” from the File Menu
Click File > Clone Repository.
3. Choose the Repository URL or GitHub.com Tab
- GitHub.com tab shows your repositories directly in a list.
- URL tab lets you paste any repository link (useful for public repos you don’t own).
4. Select the Local Path on Your Windows PC
Choose a folder on your system. This helps keep multiple repositories organized.
5. Click Clone to Download the Project
Click Clone. GitHub Desktop downloads the repository and prepares it for use. You can then manage branches, commits, and pulls visually.
Method 3: How to Clone a GitHub Repository in Visual Studio Code (VS Code)
If you already use VS Code, you don’t need to leave the editor to clone a project. This method is highly efficient for developers.
- Open VS Code.
- Press F1 or Ctrl + Shift + P to open the Command Palette.
- Type
Git: Cloneand select it. - Paste the Repository URL you copied from GitHub (or select “Clone from GitHub” to search your own repos).
- Select a folder on your computer where you want to save the project.
- Click Open when the notification appears to immediately load your project.
How to Update a Cloned Repository (Git Pull vs. Fetch)
After cloning, your local copy stays static unless you update it manually. Since repositories often change, keeping them updated is essential.
To download and merge updates:
git pull
To download updates without merging:
git fetch origin
Fetching works well when you want to review changes before applying them. Pulling remains the most common approach for daily updates.
Best Practices for Managing Cloned Repositories on Windows
Follow these best practices to avoid issues and maintain clean workflows:
- Verify remote URL:
git remote -v - List all branches:
git branch -a - Prefer SSH for long-term secure access, especially if you push code frequently.
- Pull updates before starting new work to avoid merge conflicts.
- Organize repositories into clear directories (e.g.,
C:\Users\Name\Dev). - Fork public repositories before contributing.
Pro Tip for Large Repositories: If you are cloning a massive project and only need the latest code (not the history), use a Shallow Clone: git clone --depth 1 https://github.com/username/repo.git
This downloads only the most recent commit, saving significant time and disk space.
Troubleshooting Common Git Clone Errors on Windows
Fix: HTTPS Authentication Failed (Password Support Removed)
- Error Message: “Support for password authentication was removed…”
- Fix: You must use a Personal Access Token (PAT) or update Git for Windows to use the new Credential Manager, which triggers a browser login.
Solution: “Repository Not Found” Error on Windows
- Confirm repository URL is correct.
- Check permissions for private repositories (are you logged into the correct account?).
- Verify the repository still exists and hasn’t been deleted or made private.
Fix: Permission Denied (Publickey) & SSH Key Issues
- Add SSH keys to GitHub (Settings > SSH and GPG Keys).
- Verify key permissions using
ssh -T git@github.com. - Check remote URL format (it should look like
git@github.com:user/repo.git).
Fix: Default Branch (Main vs. Master) Missing
- Many repositories now use main instead of master.
- Check available branches before cloning using the GitHub UI drop-down menu.
Most issues relate to authentication, permissions, or outdated Git installations.
Frequently Asked Questions About Cloning GitHub Repos on Windows
How do I clone a GitHub repository to a specific folder in Windows?
Navigate to the desired folder using cd, then run git clone. Alternatively, use git clone <URL> <FolderName> to specify a custom folder name.
Can I clone a private GitHub repository on Windows?
Yes, if you authenticate using HTTPS with a PAT or SSH keys.
Can I clone a GitHub repository without Git installed?
No. Git must be installed unless you use GitHub Desktop, which bundles its own version of Git.
What is the command to clone a Git repository in Windows?
git clone repository-url
Where does Git clone save files in Windows?
Git saves files in the directory where you run the clone command.
Conclusion: Start Cloning and Coding on Windows Today
If you want to work seriously with GitHub projects, cloning repositories is a must-have skill. Whether you choose Git Bash, PowerShell, Command Prompt, or GitHub Desktop, the process remains reliable and beginner-friendly.
We recommend you start by cloning projects that interest you, exploring their structure, and experimenting locally. As your confidence grows, you can move on to branching, committing, pushing, and submitting pull requests.
You’re now fully prepared to clone a repository from GitHub on Windows with confidence and clarity.
Visit Our Post Page: Blog Page
